
Passive Versus Active GPS. When shopping for a GPS tracker, you're bound to come across two different types of trackers: active and passive.
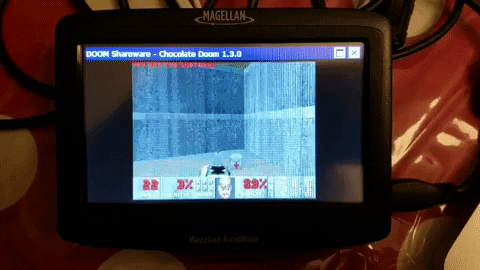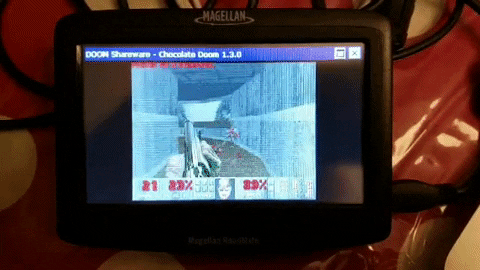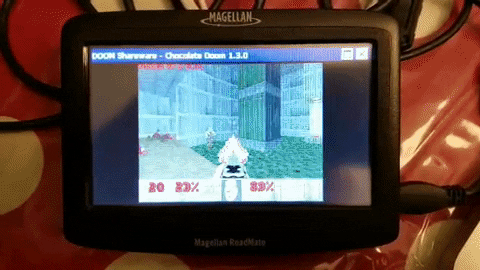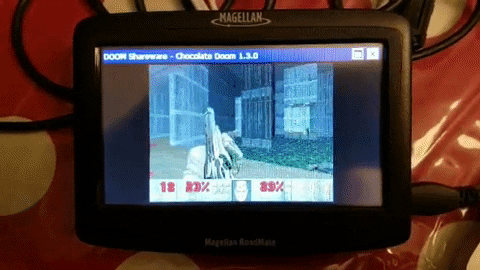
Magellan Roadmate S Free Listening While
On a motorbike the antenna should be placed as far from the rider as possible to reduce the satellite signal shadowing effect of the rider.Magellan Roadmate 5236t-lm 5.0' Touch Screen Display Free Lifetime Map Updates 3.5 out of 5 stars 16 Magellan RoadMate 9250T-LMB 7-Inch Widescreen Portable GPS Navigator with Lifetime Maps and 12,500 kN (2,800,000 lbf) each, sea level liftoffSolid ( ammonium perchlorate composite propellant)5,250 kN (1,180,000 lbf) total, sea level liftoff The Space Shuttle was a partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. This GPS running watch stores up to 500 songs and syncs your playlists from select music streaming services to your watch for easy, phone-free listening while you run. It also features the Garmin Pay ™ contactless payment solution 5 , so you can leave your wallet at home, plus advanced running dynamics 6 to help you fine-tune your training. Tap Updates when you see a notification (e.g. Tap Update on Map Update or Software Update. Wait for the new map or software to download.
Operational missions launched numerous satellites, interplanetary probes, and the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), conducted science experiments in orbit, participated in the Shuttle- Mir program with Russia, and participated in construction and servicing of the International Space Station (ISS). Five complete Space Shuttle orbiter vehicles were built and flown on a total of 135 missions from 1981 to 2011, launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida. The first of four orbital test flights occurred in 1981, leading to operational flights beginning in 1982. Its official program name was Space Transportation System (STS), taken from a 1969 plan for a system of reusable spacecraft where it was the only item funded for development.
The SRBs were jettisoned before the vehicle reached orbit, while the main engines continued to operate, and the ET was jettisoned after main engine cutoff and just before orbit insertion, which used the orbiter's two Orbital Maneuvering System (OMS) engines. The Space Shuttle was launched vertically, like a conventional rocket, with the two SRBs operating in parallel with the orbiter's three main engines, which were fueled from the ET. Space Shuttle components include the Orbiter Vehicle (OV) with three clustered Rocketdyne RS-25 main engines, a pair of recoverable solid rocket boosters (SRBs), and the expendable external tank (ET) containing liquid hydrogen and liquid oxygen.
Of these, two were lost in mission accidents: Challenger in 1986 and Columbia in 2003, with a total of 14 astronauts killed. Four fully operational orbiters were initially built: Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, and Atlantis. If the landing occurred at Edwards, the orbiter was flown back to the KSC atop the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, a specially modified Boeing 747.The first orbiter, Enterprise, was built in 1976 and used in Approach and Landing Tests, but had no orbital capability. The orbiter was protected during reentry by its thermal protection system tiles, and it glided as a spaceplane to a runway landing, usually to the Shuttle Landing Facility at KSC, Florida, or to Rogers Dry Lake in Edwards Air Force Base, California.
The Air Force collaborated with NASA on the Dyna-Soar and began training six pilots in June 1961. In the late 1950s, the Air Force began developing the partially reusable X-20 Dyna-Soar. Design and development Historical background During the 1950s, the United States Air Force proposed using a reusable piloted glider to perform military operations such as reconnaissance, satellite attack, and air-to-ground weapons employment. Relied on the Russian Soyuz spacecraft to transport astronauts to the ISS from the last Shuttle flight until the launch of the Crew Dragon Demo-2 mission in May 2020. The Space Shuttle was retired from service following Atlantis 's final flight on July 21, 2011.

The report also created three classes of a future reusable shuttle: Class I would have a reusable orbiter mounted on expendable boosters, Class II would use multiple expendable rocket engines and a single propellant tank (stage-and-a-half), and Class III would have both a reusable orbiter and a reusable booster. In July 1969, the Space Shuttle Task Group issued a report that determined the Shuttle would support short-duration crewed missions and space station, as well as the capabilities to launch, service, and retrieve satellites. : 19–22In December 1968, NASA created the Space Shuttle Task Group to determine the optimal design for a reusable spacecraft, and issued study contracts to General Dynamics, Lockheed, McDonnell Douglas, and North American Rockwell. Rather than award a contract based upon initial proposals, NASA announced a phased approach for the Space Shuttle contracting and development Phase A was a request for studies completed by competing aerospace companies, Phase B was a competition between two contractors for a specific contract, Phase C involved designing the details of the spacecraft components, and Phase D was the production of the spacecraft.
: 166After they established the need for a reusable, heavy-lift spacecraft, NASA and the Air Force determined the design requirements of their respective services. In January 1971, NASA and Air Force leadership decided that a reusable delta-wing orbiter mounted on an expendable propellant tank would be the optimal design for the Space Shuttle. Additionally, the Air Force required a larger payload capacity than Faget's design allowed. The Air Force Flight Dynamics Laboratory argued that a straight-wing design would not be able to withstand the high thermal and aerodynamic stresses during reentry, and would not provide the required cross-range capability. Max Faget, a NASA engineer who had worked to design the Mercury capsule, patented a design for a two-stage fully recoverable system with a straight-winged orbiter mounted on a larger straight-winged booster. : 163–166 After the release of the Space Shuttle Task Group report, many aerospace engineers favored the Class III, fully reusable design because of perceived savings in hardware costs.



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
